Hydatid Disease of The Brain Parenchyma: A Systematic Review
Abstarct
Introduction
Isolated brain hydatid disease (BHD) is an extremely rare form of echinococcosis. A prompt and timely diagnosis is a crucial step in disease management. This study is a systematic review of studies on intra-parenchymal BHD.
Methods
Studies that had the following properties were included: 1) The intra-parenchymal brain infection had been confirmed by diagnostic modalities, surgical findings, or histopathology. 2) The patient details were provided in the study. 3) The cystic lesion [s] were located intracranially.
Results
Altogether, 112 studies with a sample size of 178 cases met the inclusion criteria. Males (60.1%) showed a higher prevalence of the disease than females (38.2%). Most of the cases (64%) were affected during the first and second decades of their lives. Left-side multi-lobe involvement was the most common type of involvement (28.1%), followed by right-side multi-lobe involvement (26.4%). Surgery was the primary treatment option (97.2%), with the Dowling technique or the modified Arana-Iniguez method as the preferred approach. The total recurrence and mortality rates were 7.3% and 3.4%, respectively.
Conclusion
The definitive treatment for BHD is surgery, with the aim of removing cysts intact or excising mass lesions completely. A history of cyst rupture during operation may increase the likelihood of recurrence, and an extensive follow-up is required.
Introduction
Hydatid disease (HD) is a parasitic infection caused by the larvae of the tapeworm Echinococcus. Different genera of this microorganism can cause disease; however, in humans, two species have major clinical sequelae. Echinococcus granulosus results in cystic disease, the most common type, while Echinococcus multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis (AE), presenting as a mass or cystic lesion. The latter form of the disease is more invasive and aggressive, accompanied by numerous diagnostic and management challenges [1-3]. The most common organs affected by hydatidosis are the liver and lungs. However, other parts of the body can also be affected, including the bones, pericardium, orbits, ovaries, central nervous system (CNS), and other organs. In the literature, 2–3% of cases show involvement of the CNS. The incidence of isolated brain involvement is reported to be 1–2% of all cases of echinococcosis, representing approximately 2% of all intracranial space-occupying lesions [4-6]. Brain hydatid disease (BHD) is endemic in many regions where livestock raising is prevalent, and human-animal contact is common. The incidence varies geographically, with higher rates reported in rural areas. However, globalization and increased travel have led to sporadic cases being reported in non-endemic regions as well. Humans can become infected through the ingestion of parasite eggs in contaminated food, water, or by direct contact with infected dogs, canines, and sheep [7,8]. Most cases of intracerebral echinococcosis are diagnosed in pediatrics (50-75%) [9]. The clinical presentation of hydatidosis depends on the patient's age, the size, number, and location of the cyst, as well as the host's immune system. Patients with HD can remain asymptomatic for long periods, as the lesions take years to develop. When they grow well, intracranial hypertension secondary to the mass effect on the surrounding tissues is usually the first clinical sign of brain involvement. The disease may not cause focal neurological signs until they become enlarged [10-12]. In the literature, several reviews have been published on cerebral HD; however, there is a scarcity of systematic reviews on the topic. This study is a systematic review of studies on intra-parenchymal BHD published over the last two decades [1-112].
Methods
Study design and reporting standards
The study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.
Search strategy
A systematic review of all published studies on brain parenchymal HD was conducted from 2000 to 2024 using the following databases: Google Scholar, PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, Science Direct, and EMBASE. The keywords used in the search included:
[brain OR intraparenchymal OR cerebral OR intracerebral OR cerebrum] AND [hydatid OR hydatidosis OR echinococcoses OR echinococcosis OR echinococcal OR echinococcus].
Eligibility criteria
Non-English language studies and those unrelated to humans were excluded before or during the initial screening. Studies of BHD were included if: 1) Diagnostic modalities, surgical findings, or histopathology confirmed the intraparenchymal brain infection. 2) Patient details were provided in the study. 3) Studies published in predatory journals (inappropriately peer-reviewed) and those not meeting inclusion criteria were excluded [113].
Study selection
Titles and abstracts of identified studies were initially screened, followed by full-text screening to assess eligibility.
Data extraction
Data extracted from eligible studies included study design, country of study, patient age, gender, residency, symptoms, medical history of HD, cyst characteristics, diagnosis, management, follow-up, and outcomes.
Data analysis
Data were analyzed qualitatively (descriptive analysis) using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 27.0 software
Results
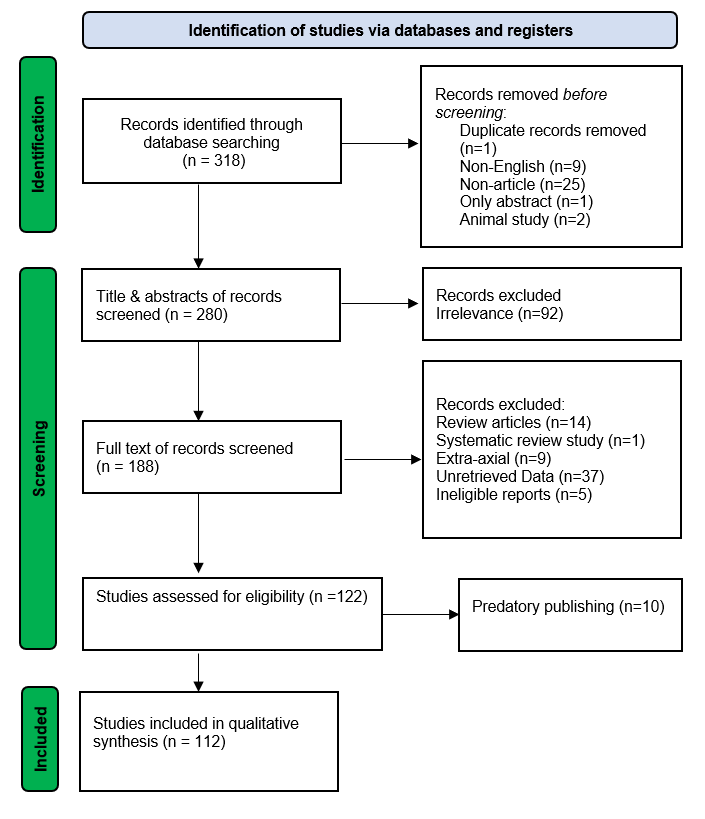
In total, 318 studies were obtained from the resources. Before any screening, 38 of them were directly excluded due to duplication, non-English language, non-articles, and animal studies. Following the initial screening, 92 studies did not meet the inclusion criteria and were excluded. The remaining 188 studies underwent full-text screening, and 122 of them were assessed for eligibility. Ultimately, 112 studies (comprising 178 cases) met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1). The characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1. Out of these studies, 101 (90.2%) were case reports, 10 (8.9%) were case series, and one (0.9%) was a retrospective cohort study. Most of the cases were reported in Turkey (24.1%), followed by Iran (16.7%), India (15.2%), and Morocco (9.8%). Males (60.1%) showed a higher prevalence of the disease than females (38.2%). Most of the cases (64%) occurred in the first and second decades of life, with a mean age of 20.44 ± 16.76 years. There were 71 cases (39. 9%) in rural areas and eight cases (4.5%) in urban areas. The residency of the remaining 99 cases (55.6%) was not reported. The type of the disease was cystic in 158 cases (88.8%) and alveolar in 20 cases (11.2%). Thirteen (7.3%) cases had a previous history of HD. The most commonly presented symptoms were signs of raised intracranial pressure, including headache (62.9%), vomiting (43.3%), followed by seizure (30.3%) and paresis (28.7%). Multiple organ involvement was present in 48 (27%) cases, involving the lung, liver, kidney, adrenal gland, blood vessels, or bones. The disease was primary with a single cyst or lesion in 118 patients (66.3%), primary with multiple cysts in 27 (15.1%), secondary with a single cyst in 23 (13%), and secondary with multiple cysts in 10 (5.6%). Left-side multi-lobe involvement was the most common type of involvement (28.1%), followed by right-side multi-lobe involvement (926.4%) and parietal lobe involvement (18.5%).
Serology had been done in 55 cases (30.9%), and it was positive in 34 (19.1%). Computed tomography scans (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were used in all cases. Surgery was the main treatment option (97.2%). The Dowling technique, or modified Arana-Iniguez, was the method of choice (95.5%). Surgery in three cases (1.7%) was done through the Burr-hole technique instead of open craniotomy. Conservative management was performed in five cases (2.8%). The patients underwent follow-up with a mean interval of one year. Recurrence was reported in 13 cases (7.3%). Among those, six cases (46.1 %) had intra-operative complications of traumatic rupture of the cyst, and two cases (15.4 %) had a surgical puncture of the cyst. The remaining five cases (38.5%) did not experience any intraoperative complications. The mortality rate was 3.4% (Table 2).
|
Author |
Country |
Study design |
No |
Age |
Sex |
Presenting symptoms |
Imaging |
ISHC |
No. of cyst [s] in brain |
Location of cyst [s] in brain |
Size [cm] |
Serology |
Type of management |
Pre-Op complication |
Intra-Op complication |
Post-Op complication |
Adjuvant therapy |
Follow up* outcome |
|
Svrckova et al [1] |
United Kingdom
|
Case report
|
3 |
30 |
M |
Headache, seizure |
MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parietal, right temporal |
N/A |
Positive |
Conservative [Albendazole/praziquantel/steroid/antiepileptic] |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
None |
Improved |
|
26 |
M |
Collapse, slurred speech, seizure, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal and basal ganglia |
N/A |
Positive |
Conservative [Albendazole/Praziquantel/steroid/Antiepileptic] |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
None |
Improved |
||||
|
37 |
M |
Dry cough |
MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Bilateral hemisphere |
N/A |
Positive |
Conservative [Albendazole] |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
None |
Improved |
||||
|
Altibi et al [2] |
Brazil |
Case report |
1 |
13 |
M |
Headache, nausea |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
4.7 |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling]/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Casulli et al [3] |
Italy |
Case report |
1
|
6 |
M |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
6.8 |
Negative |
Surgical removal/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
Seizure, headache, worsened right hemiparesis, peri-lesional edema |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic,Steroid |
Improved |
|
Lakhdar et al [4] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
30 |
M |
Headache, right side hemiparesis |
MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal |
None |
Rupture of cysts |
None |
Albendazole, Antibiotics, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
Fariba Bi. [5] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
18 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, anticonvulsant |
Recovered |
|
Saleh et al [6] |
Egypt |
Case series
|
4 |
9 |
M |
Drowsiness, vomiting, blurred vision, headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
10 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
12 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
14 |
F |
Headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
Alomari et al [7] |
Saudi Arabia |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Bilateral exophthalmos, blurred vision, headache |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left frontal |
15.3
|
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
Seizure |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Hafedh et al [8] |
Iraq |
Case report |
1 |
27 |
M |
Seizure, headache, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right hemisphere |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Umut et al [9] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
14 |
M |
Double vision, headache nausea, vomiting |
MRI |
Yes |
2 |
Left occipital lobe, right insula |
1st: 5.6 2nd:2.6 |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] first occipital cysts and after 6 m temporal insula |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Çavusoglu et al [10] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Left side hemiparesis, left side mouth deviation, slurred speech |
CT, Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
10.2
|
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Garg et al [11]
|
India |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Left side hemiparesis, left side mouth deviation, slurred speech |
CT, Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
10.2
|
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Raouzi et al [12] |
Morocco
|
Case series
|
4 |
14 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal area |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
4 |
M |
Headache, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
7.05 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
3 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal lobe |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
22 |
F |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
Assefa et al. [13]
|
Ethiopia |
Case series
|
4 |
8 |
M |
Hemiparesis, nausea and vomiting |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal + daughter cyst |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical Removal |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
Cystic abscess, peri-cystic vasogenic edema |
N/A |
Recurrence |
|
5 |
F |
Hemiparesis, nausea and vomiting |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical Removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
||||
|
10 |
F |
Hemiparesis, nausea and vomiting |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical Removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
||||
|
29 |
M |
Hemiparesis, nausea and vomiting |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical Removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
||||
|
Tanki et al [14]
|
India |
Case series |
9 |
10 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
12 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
||||
|
12 |
M |
Seizure, headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
10 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
11 |
M |
Seizure, hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
16 |
F |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
14 |
M |
Seizure, hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
||||
|
7 |
F |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
12 |
F |
Seizure, hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
Noori et al [15] |
Iraq |
Case report |
1 |
26 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Haradhan et al [16] |
Bangladesh |
Case report |
1 |
14 |
M |
Headache |
Contrast CT, Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
12.48 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Right frontoparietal subdural hygroma, hydrocephalus, pseudocyst |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Panda et al [17] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
4 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
4.47 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Sharifi et al [18] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
44 |
M |
Mood swings, restlessness, and headache |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontoparietal lobe |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Aydin et al [19] |
Turkey |
Case series |
2 |
9 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, bilateral decreased vision, left side tremor, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parietal |
9.81 |
Negative |
Surgical removal [cavity placed balloon/ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
18 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, blurred vision, fever, quadriparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parietal |
8.96 |
Negative |
Surgical removal [cavity placed balloon/ Dowling-Orlando] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
||||
|
Çakir et al [20] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
6 |
M |
Headache |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Cardiac arrest/death |
N/A |
N/A |
Death |
|
Ponnambath et al [21] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
40 |
M |
Headache, seizure |
Contrast MRI |
No |
1 |
Left occipital lobe |
3 |
N/A |
Surgical removal/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Minimal visual field defect |
|
İzgi et al [22] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, deviation of the eyes |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal lobe |
6.92 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
El Ouarradi et al [23] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
11 |
M |
Nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parieto-temporal lobe |
9.75 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Shock/cardiac arrest/death |
N/A |
N/A |
Death |
|
Baboli et al [24] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
19 |
M |
Headache, left hemiparesis |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal lobe |
8 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Arega et al [25] |
Ethiopia |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Headache, vomiting |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporal |
13.27 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Altaş et al [26] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
26 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
Contrast CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
7.95 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Madeo et al [27] |
USA |
Case report |
1 |
82 |
F |
Emergency case |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left hemisphere |
4.08 |
Positive |
Conservative [Albendazole] |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
None |
Stable cyst |
|
Menschaert et al [28] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
F |
Seizures |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
Puncture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Learning disabilities |
|
Şule et al [29] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
83 |
M |
Headache, forgetfulness |
Contrast MRI |
No |
1 |
Right frontal lobe |
4 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Benhayoune et al [30] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
18 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, seizure |
Contrast MRI |
No |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
7.9 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
Vikaset al [31] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
20 |
M |
Seizure, right side paresthesia, headache, vomiting |
Contrast CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Reddy et al [32] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
35 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, altered sensorium, loss of consciousness |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
5
|
Both parietal lobes |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Al-Rawi et al [33]
|
Iraq
|
Case series
|
8 |
3.5 |
F |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
7 |
F |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
Delayed recovery |
Antiepileptic |
Recurrence |
||||
|
11 |
M |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
13 |
F |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal lobe |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
15 |
M |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
15 |
M |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
35 |
M |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
14 |
F |
N/A |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
Naderzadeh et al [34] |
Iran |
Case report
|
1 |
12 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, decreased vision |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
4.56 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Visual deficit |
Albendazole |
Myopia, occasional seizure |
|
Shafiei et al [35]
|
Iran
|
Case series
|
3 |
3 |
M |
Headache |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parietal |
5.83 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
59 |
F |
Headache, fever |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
8.48 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
||||
|
53 |
F |
Angiopathy, nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recurrence |
||||
|
Nechi et al [36] |
Tunisia |
Case report |
1 |
50 |
F |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal lobe |
4.97 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Ekici et al [37] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
12 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, diplopia |
CT |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling]/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Bagheri et al [38] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
18 |
M |
Nausea,vomiting, right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporal |
6 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Bušić et al [39] |
Croatia |
Case report |
1 |
37 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, balance difficulties, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
5
|
Right parietal lobe |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Wound infection and osteomyelitis |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
|
Nashibi et al. [40] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
59 |
M |
Disorientation, right side hemiparesis, headache, dysarthria |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-temporal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Improved |
|
Ammor et al [41] |
Morrocco |
Case report |
1 |
4 |
N/A |
Weakness, headache, vomiting |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Headache, subdural hygroma |
|
Alok et al [42] |
Syria |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
F |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Pons |
2.1 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling-Orlando] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Chatzidakis et al [43] |
Greece |
Case report |
1 |
27 |
M |
Quadriparesis, headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Bilateral frontal, bilateral occipital, cerebellum |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [3 times] |
None |
None |
Generalized seizure post 1st OP |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Panagopoulos et al [44] |
Greece |
Case report |
1 |
11 |
M |
Headache, vomiting |
Contrast CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
6.85 |
Negative |
Surgical removal/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Karaaslan et al [45] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
22 |
M |
Nausea,vomiting, headache |
CT,MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
6.92 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Hajhouji et al [46] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
17 |
F |
Seizure |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Tascu et al [47] |
Romania |
Case report |
1 |
3 |
N/A |
Post cranio-cerebral trauma |
Contrast CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parieto-occipital lobe |
10 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Subdural hematoma |
|
Ghaemi et al [48] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
28 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT,MRI |
No |
1 |
Right temporal |
6 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Ganjeifar et al [49] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
13 |
M |
Fever ,abdominal pain |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Nemati et al [50] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
6 |
M |
Ataxia, left side hemiparesis |
CT,MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
13.29
|
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Mehrizi et al. [51] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Fronto-parietal |
10
|
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Fakhouri et al [52] |
Syria |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, difficult walking |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right Cerebellum |
6
|
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Ghasemi et al [53] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Malaise, vomiting, headache |
CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parieto-occipital |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Mallik et al. [54] |
India
|
Case report |
2
|
10 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, right side hemiparesis, aphasia |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parietal |
10.32
|
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole, Antibiotics, Antiepileptic, Steroids |
Improved |
|
16 |
M |
Decreased vision, headache, vomiting |
CECT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-temporo-parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Seizure, unconsciousness |
||||
|
Arora et al[55] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
9 |
F |
Seizure, decreased vision, headache, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal lobe |
7.23 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Al-Musawi et al [56] |
Iraq |
Case report |
1 |
14 |
F |
Seizure |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Burr-hole surgical removal |
Deterioration in the consciousness, right side hemiparesis, apnea |
None |
None |
Albendazole, anticonvulsant |
Recovered |
|
Ghasem et ali [57] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
30 |
F |
Seizure, headache, intellectual impairment, abnormal behavior |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Polat et al. [58] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
45 |
M |
Personality disorder, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recurrence & Death |
|
Hmada et al [59]
|
Morocco |
Case report |
2 |
5 |
F |
Decreased vision, tremor |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Improved |
|
5 |
F |
Right side heaviness |
N/A |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, anticonvulsant |
Recovered |
||||
|
Senapati, et al [60]
|
India |
Case report |
2 |
22 |
M |
Vomiting, disorientation |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Cyst wall puncture |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
40 |
M |
Seizure, headache, vomiting, right side hemiparesis |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
||||
|
Imperato et al [61] |
Italy |
Case report |
1 |
9 |
M |
Headache, diplopia |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Ramosaço et al [62] |
Albania |
Case report |
1 |
22 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, seizure |
MRI |
Yes |
6
|
Left frontal lobe, left frontal-parietal, left temporo-parietal, right occipital and right frontal |
1st:2.79 2nd:4.18 3rd:4.29 4th:2.89 5th:4.09 6th:2.84 |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Encephalomalacia |
|
Ravanbakhsh et al [63] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
12 |
M |
Vision disturbance |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
8 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Pulavarty [64] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
16 |
F |
Generalized seizure |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-temporal |
4.89 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Shastry et al. [65] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
7 |
F |
Blurred vision |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-temporal |
5.65 |
N/A |
surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Chen et al [66] |
China |
Case report |
1 |
28 |
F |
Seizure |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
Positive |
Conservative [Albendazole] |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
None |
Size of the cyst reduced |
|
Kaushik et al [67] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
53 |
M |
Seizure exacerbation |
CT |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Wani, et al [68] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
13 |
M |
Generalized seizure, vomiting |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right occipital |
8.48 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Armanfar et al [69] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
46 |
F |
Headache, blurred vision |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
Rupture of cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Khan et al [70] |
Pakistan |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
M |
Headache, fever, vomiting |
Contrast MRI |
Yes |
19 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Steroid, Antibiotic, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
Charles et al [71] |
Congo |
Case report |
1 |
32 |
N/A |
Seizure, vomiting |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
2 |
Bilateral hemisphere, right temporo-parietal |
1st:1.02 2nd:6.87 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Steroid |
Improved |
|
Garg et al. [72] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
47 |
M |
Headache, vomiting |
MRI |
Yes |
7
|
Both sides of cerebrum |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Disturbed verbal output |
|
Abuhajar et al [73] |
Libya |
Case report |
1 |
50 |
M |
Headache, left side numbness, left toes paresthesia, vomiting |
Contrast CT, MRI |
Yes |
3
|
Right temporo-parietal |
1st: 3.5 2nd: 3.8 3rd: 4.0 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Umerani et al. [74] |
Pakistan |
Case report |
1 |
22 |
F |
Headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Touzani et al. [75] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
M |
Vomiting , weakness, seizure |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Kibzai et al [76] |
Pakistan |
Case series |
3 |
10 |
M |
Left side paresthesia, nausea |
CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Puncture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recurrence |
|
40 |
M |
Vomiting, altered behavior |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
72 |
M |
Seizure, personality disorder |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
32 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
Duransoy et al [77] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
13 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
10 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
Left hemiparesis, subdural hygroma |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Qureshi et al [78] |
Pakistan |
Case report |
1 |
11 |
M |
Seizure |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left posterior-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Senol et al. [79] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
6 |
F |
Headache with photophobia and phonophobia |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontotemporal |
10.5 |
Negative |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
Kandemirli et al [80] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
6 |
M |
Nausea, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal extended to lateral ventricle |
7.95 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole, Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
Bahannanet al [81] |
Yemen |
Case report |
1 |
17 |
M |
Imbalance, ataxia, falls, right side hemiparesis, fever, headache, decreased visual acuity, diplopia. |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
5 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Kumar et al [82] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
25 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, right side weakness, seizure |
Contrast CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Agrawal et al [83] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
25 |
M |
Difficulty walking, seizure |
CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
24.63 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
|
Mustafa et al [84] |
Iraq |
Case report |
1 |
2 |
M |
Focal seizure |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
6 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
none |
Recovered |
|
IJaz et al [85] |
Pakistan |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
M |
Headache, fever, right-side hemiparesis, difficult walking |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left cerebrum |
8.94 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Borni et al [86] |
Tunisia |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
M |
Headache, vomiting |
CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
2
|
Left occipital |
1st: 3.39 2nd: 2.25 |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
Puncture of Cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Kojundzicet al [87] |
Croatia |
Case report |
1 |
34 |
F |
Headache, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
3
|
Right temporo-parietal |
1st:3.8 2nd:2.9 3rd: N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Osteomyelitis |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Siyadatpanah et al [88] |
USA |
Case report |
1 |
39 |
M |
Right side paresthesia, imbalance |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Akrim et al [89] |
Morocco |
Case report |
1 |
22 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, blurred vision |
CT |
Yes |
>1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Arana] |
None |
None |
Neurological deficit |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Zeynal et al [90] |
Turkey |
Retrospective cohort
|
12 |
50 |
M |
Headache, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 4 |
|
55 |
M |
Dysarthria, focal seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
40 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 4 |
||||
|
26 |
M |
Headache, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
35 |
F |
Headache, right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left thalamus |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
25 |
M |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left thalamus |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 4 |
||||
|
64 |
M |
Dysphasia |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Death |
||||
|
27 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, altered consciousness |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
13 |
M |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
62 |
M |
Left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Death |
||||
|
49 |
M |
Headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
52 |
M |
Headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
2
|
Left temporal, right frontal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Albendazole |
Glasgow outcome: 5 |
||||
|
Ozdol et al [91] |
Croatia |
Case report |
1 |
23 |
M |
Nausea, imbalance, headache, urinary and fecal incontinence |
MRI |
No |
1 |
Left cerebellum |
2.08 |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Ma et al [92]
|
China |
Case report |
2 |
50 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
Contrast CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
2
|
Right frontal, left temporal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
42 |
F |
Headache, vomiting |
Contrast CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
2
|
Left frontal, left temporal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
Mokhtari et al [93] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
60 |
F |
Headache, bilateral decreased vision, delusions, cognitive disorders |
Contrast CT, MRI |
Yes |
2
|
Left fronto-parietal, right parieto-occipital |
1st: 3 2nd: 2.08 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Benzagmout et al [94]
|
Morrocco
|
Case report |
2 |
21 |
F |
Seizure |
Contrast CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Antiepileptic |
Recovered |
|
24 |
F |
Headache, vomiting |
CT |
No |
1 |
Right frontal |
4.47 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
Ray et al [95] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
4 |
M |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, altered sensorium, fever |
CT |
Yes |
>1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
N/A |
N/A |
Meningitis, subdural effusion, hydrocephalus |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Yiş et al [96] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
7 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, myalgia, abdominal pain |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Temporo-parieto-occipital |
8 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Mebendazole |
Recovered |
|
Per et al [97]
|
Turkey |
Case series
|
5 |
15 |
M |
Headache, intellectual impairment, dysphasia |
CT |
Yes |
4
|
Left fronto-parietal , left occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recurrence & Death |
|
15 |
M |
Headache, faintness, diplopia, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
4 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, seizure |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
||||
|
16 |
M |
Vomiting , seizure, headache |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
11 |
M |
Headache, vomiting, strabismus |
MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Right occipital,right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [ Dowling]/neuronavigation |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Improved |
||||
|
Radmenesh et al [98] |
Iran |
Case report |
2 |
7 |
F |
Headache,vomiting, right side hemiparesis |
CT |
Yes |
4
|
Left frontal |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Hydrocephalus |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
12 |
M |
Headache,vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporal |
N/A |
Negative |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
Balak et al [99] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
16 |
M |
Headache, visual disturbance |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
6 |
Positive |
Surgical removal/microsurgery |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Najjar et al [100] |
Saudi Arabia |
Case report |
1 |
11 |
M |
Left side hemiparesis |
CT, contrast MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right hemisphere |
8 |
Negative |
Burr-hole surgical removal |
None |
Puncture of Cyst |
Abscess at surgical site |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Tatli et al [101] |
Turkey |
Case report |
3 |
7 |
M |
Headache, left side hypoesthesia |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
7.65 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
15 |
F |
Headache, vomiting |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
8.48 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
||||
|
10 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, left side weakness |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right fronto-temporo-parieto-occipital |
10.32 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
N/A |
||||
|
Yurt et al [102] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
19 |
F |
Headache, vomiting, seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Bilateral hemispheres |
N/A |
Negative |
Multiple surgeries |
Left side hemiplegia, deterioration |
None |
Recurrence of symptoms |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
|
Aydin et al[103] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
7 |
M |
Headache,behavioral disturbance, counting and calculation disorders, mental regression |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parietal |
7.48 |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
Left hemiparesis |
Mebendazole |
Recovered |
|
Tuzun et al [104] |
Turkey |
Case series |
13 |
9 |
M |
Headache, seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
Deterioration |
None |
Subdural effusion |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
5 |
M |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
Porencephalic cyst |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
16 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parieto-occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
11 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
Cerebral spinal fluid collection |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
12 |
M |
Left side hemiparesis, seizure |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right frontal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
Deterioration |
None |
Subdural effusion |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
8 |
F |
Headache, loss of consciousness |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
Deterioration |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
3 |
M |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
Deterioration |
None |
Subdural effusion |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
17 |
M |
Headache, left side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
18 |
M |
Headache, right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
Hemorrhage |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
16 |
F |
Right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
>1 |
Left occipital, left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
Rupture of cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
||||
|
11 |
M |
Headache |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
9 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right occipital |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
Hemorrhage |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
5 |
F |
Headache, right side hemiparesis |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
||||
|
Bakaris et al [105] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
8 |
F |
Right upper paresis, headache |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left temporo-parieto-occipital |
8.14 |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Guney et al [106] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
18 |
M |
Headache, neck pain |
CT |
Yes |
1 |
Left fronto-parietal |
N/A |
Positive |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Önal et al [107] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
7 |
F |
Ataxia, apraxia, Headache, tremor |
CT, MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Right temporo-parietal |
6.21 |
N/A |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Muthusubramanian et al [108] |
India |
Case report |
1 |
40 |
F |
Headache, right side hemiparesis, double vision, gait abnormality |
Contrast CT |
Yes |
1 |
Pons |
N/A |
N/A |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Improved |
|
Kabatas et al [109] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
26 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting, seizure |
MRI |
Yes |
1 |
Left frontal |
4.13 |
Positive |
Surgical removal [Dowling] |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Improved |
|
Menkü et al [110] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
35 |
M |
Seizure |
CT, MRI |
No |
1 |
Righ parieto-occipital |
4.74 |
Negative |
Surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
Recovered |
|
Anvari et al [111] |
Iran |
Case report |
1 |
5 |
F |
Headache, nausea, vomiting |
Contrast CT |
No |
1 |
Right fronto-parietal |
N/A |
N/A |
Burr-hole surgical removal |
None |
None |
None |
Albendazole |
Recovered |
|
Karadag˘et al [112] |
Turkey |
Case report |
1 |
45 |
F |
Seizure, confusion |
CT |
Yes |
2 |
Left fronto-parietal, right parietal |
5 |
Negative |
Surgical removal |
Deterioration |
Puncture of the left cyst |
None |
Albendazole |
Recurrence |
|
CT; computed tomography, MRI; magnetic resonance imaging, ISHC; Imaging suggested hydatid cyst, N/A; non-available, OP; operative, *Improved = Symptomatic improvement but not complete recovery during the follow-up period. Recovered = Complete recovery/free of symptoms. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Variables |
Frequency/Percentage |
|
|
Country of study Turkey Iran India Morocco Iraq Pakistan Croatia Others |
27 (24.1%) 19 (16.7%) 17 (15.2%) 11 (9.8%) 5 (4.6%) 5 (4.6%) 3 (2.7%) 25 (22.3%) |
|
|
Study design Case Report Case Series Retrospective cohort |
101 (90.2%) 10 (8.9%) 1 (0.9%) |
|
|
Age, year, mean [SD] |
20.44± 16.76 |
|
|
Age group ≤9 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 |
52 (29.2%) 62 (34.8%) 24 (13.5%) 12 (6.7%) 12 (6.7%) 10 (5.6%) 3 (1.7%) 1 (0.6%) 2 (1.1%) |
|
|
Gender Male Female N/A |
107 (60.1%) 68 (38.2%) 3 (1.7%) |
|
|
Residency Rural Urban N/A |
71 (39.9%) 8 (4.5%) 99 (55.6%) |
|
|
Previous history of hydatid disease Yes No N/A |
13 (7.3%) 161 (90.5%) 4 (2.2%) |
|
|
Type of hydatid disease Cystic Alveolar |
158 (88.8%) 20 (11.2%) |
|
|
Presentation Symptomatic Asymptomatic |
168 (94.4%) 10 (5.6%) |
|
|
Presenting complaint Headache Vomiting Nausea Seizure Paresis Impaired vision Impaired conscious level Speech abnormalities * Fever Altered sensorium ** Psychological disturbance Other symptoms |
112 (62.9%) 77 (43.3%) 35 (19.7%) 54 (30.3%) 51 (28.7%) 23 (13%) 12 (6.7%) 10 (5.6%) 8 (4.5%) 8 (4.5%) 7 (4.0%) 31 (17.4%) |
|
|
Duration of presenting symptoms [mean] |
19 weeks |
|
|
Multiple organ involvement Yes No N/A |
48 (27%) 128 (71.9%) 2 (1.1%) |
|
|
Site of the cyst/lesion [s] Left-side multi-lobe involvement Right-side multi-lobe involvement Bilateral multi-lobe involvement Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Occipital lobe Left Hemisphere [unspecified location] Right Hemisphere [unspecified location] Other [Cerebellum, Thalamus, Pons] |
50 (28.1%) 47 (26.4%) 11 (6.2%) 17 (9.6%) 33 (18.5%) 5 (2.8%) 4 (2.2%) 2 (1.1%) 2 (1.1%) 7 (4%) |
|
|
Disease status per number of cysts/lesions Primary-solitary Primary-multiple Secondary-solitary Secondary-multiple |
118 (66.3%) 27 (15.1%) 23 (13%) 10 (5.6%) |
|
|
Neurological+/-other physical examination Normal Positive findings N/A |
30 (16.8%) 92 (51.7%) 56 (31.5%) |
|
|
CT/MRI Findings Suggesting hydatid disease Not suggesting hydatid disease |
170 (95.5%) 8 (4.5%) |
|
|
Serology Positive Negative N/A |
34 (19.1%) 21 (11.8%) 123 (69.1%) |
|
|
Type of management Conservative Surgical/Open *** Burr-hole |
5 (2.8%) 170 (95.5%) 3 (1.7%) |
|
|
Disease outcome Death Survived N/A |
6 (3.4%) 139 (78.1%) 33 (18.5%) |
|
|
Recurrence Recurrence alive Recurrence dead |
11 (6.2%) 2 (1.1%) |
|
|
* Speech abnormalities: aphasia, apraxia of speech, dysphonia, slurred speech, and others. **Altered sensorium: paresthesia, numbness, and heaviness. *** Surgical removal by (Dowling technique, modified Arana-Inguinz technique, surgical removal under neuronavigation, and microsurgery). |
||
Discussion
The World Health Organization (WHO) has categorized human echinococcosis under the umbrella of tropical neglected diseases (TNDs) that require control, as the disease remains a significant health issue in endemic regions [1].
Domestic dogs serve as the primary definitive hosts for both species of Echinococcus and pose the highest risk of transmitting cystic and alveolar echinococcosis to humans. Infection in dogs occurs when they consume livestock offal containing hydatid cysts, after which they release parasite eggs in their feces, contaminating soil, water, and grazing fields. Livestock acquire the infection by ingesting these eggs during grazing, while humans are most often infected through eating or drinking contaminated food or water [114,115].
In this systematic review, studies on two genera of clinical interest, Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus multilocularis, have been reviewed. Several mechanisms have been proposed for the migration of Echinococcus larvae to the brain. Larvae hatching from ingested eggs in the intestine enter the portal circulation, spreading to different tissues where they develop hydatid disease. Two barriers can protect against CNS involvement: the first is the liver through portal circulation, and the second is the lung, which may act as a secondary filter. The lack of these effective sieves, problems in the immune system, special architecture of brain tissue, disrupted capillaries in the lungs, and structural heart diseases such as patent ductus arteriosus and patent foramen ovale may all provide a gateway to the brain [10,11]. This disease commonly affects supratentorial regions of the brain, specifically within the distribution of the middle cerebral artery, primarily targeting the parietal and frontal lobes [77,78,107]. Generally, BHD is classified as “primary” or “secondary”. The primary disease is rare; it results from direct infestation of the brain without the involvement of other organs. It most often presents as a solitary, spherical, and unilocular cyst surrounded by a broad capsule, which usually contains protoscoleces and renders a fertile lesion. The secondary type is typically characterized by multiple cerebral cysts that result from the rupture of a cyst in other organs. They lack brood capsules and protoscoleces, rendering them infertile. Therefore, the risk of recurrence after their rupture is negligible. However, on rare occasions, multiple primary cysts can occur within the brain parenchyma due to multiple larval intakes in patients with defective immune systems, metastatic deposits from the rupture of a primary cyst in the brain, or the presence of cardiac anomalies. On the other hand, alveolar disease tends to result in multiple intracerebral lesions and might resemble and behave as a malignant lesion [90-93]. Cerebral HD is considered a childhood disease, most commonly (50–75%) seen in children and young adults. Additionally, patients with cerebral HDs may also have concomitant cysts in other organs, although this occurs in less than 20% of patients with intraparenchymal hydatidosis [5,6,105].
In this systematic review, most of the cases (64%) were affected during their first and second decades of life. Multiple cysts or lesions were present in about 21% of the cases. Among these, 15.1% were primary multiple diseases, while only 5.6% of the cases had secondary multiple hydatidosis. Thus, the findings of this review disagree with the assumption that primary multiple BHD is rarer than secondary multiple lesions. Additionally, 48 cases (27%) had concomitant disease in other organs.
Signs of raised intracranial pressure (headache, nausea, vomiting) and focal neurological deficits are the most common presentations of the disease. Seizures, visual disturbances, and cranial nerve involvement are also common presenting complaints reported in the literature [103,104]. In this study, headache was the most common presenting symptom (62.9%), followed by vomiting (43.3%), similar to the other reported studies. Seizure, paresis, nausea, and visual disturbance were reported in 30.3%, 28.7%, 19.7%, and 13% of the cases, respectively. The mean duration of symptoms at the time of presentation was 19 weeks.
Timely diagnosis of BHDs is crucial because failure to make a prompt diagnosis could result in fatal consequences. Moreover, handling the cystic or mass lesion during surgical intervention is essential for reducing intraoperative complications and preventing disease recurrence. It has been declared that serological testing for the diagnosis of HD is of limited accuracy. Therefore, it is not sufficient on its own to confirm the diagnosis of HD [104]. Imaging modalities are the mainstay of diagnosis in patients with suggestive history and clinical findings, even when serological tests are negative. The disease generally poses common characteristics and pathognomonic features on scanners. Typically, CT and MRI are the primary imaging techniques, which can often be sufficient to achieve a diagnosis. For BHD, the main appearance on CT is a round, intra-parenchymal, usually large cystic lesion with a well-defined border. The cyst fluid is typically isodense or slightly hyperdense compared to cerebrospinal fluid. Calcifications or septations may or may not be present. Calcifications are primarily peri-cystic, giving a 'ground-glass' appearance, suggesting infection or damage before the larva's death. The MRI scans show a thin-walled spherical cyst containing fluid with cerebrospinal fluid characteristics on all sequences. Rim wall contrast enhancement and peripheral edema are much less common in hydatid cysts, and when present, may suggest other radiological differential diagnoses. The presence of multiple small daughter endocysts, characteristic of cystic echinococcosis, is the key distinguishing feature from other cystic lesions in the brain [1-4]. There are a few reports on the CT and MRI appearance of cerebral AE. The lesions may appear as solid, semisolid, or lobulated cystic or mass lesions with definite margins. Calcifications are usually scattered throughout the lesion, unlike in CE, where they are mainly confined to the pericystic region. Predominant features include surrounding edema and various types of contrast enhancement, such as peripheral ring-like, heterogeneous, nodular, and cauliflower-like patterns, indicating an inflammatory reaction around the lesion. Diffusion-weighted MRI is useful in distinguishing lesions from edema. Therefore, the diagnosis should be based on evidence of a primary focus in another location, an appropriate clinical history, the prevalence of the infection in the host's geographic location, and laboratory findings, as a standard practice for diagnosing and differentiating cerebral AE [90-94]. Following laboratory tests and imaging, a histopathological examination confirms the final diagnosis [80,97]. Regarding the findings of this systematic review, a serology test was performed in 30.9% of the studies, and it was positive in 19.1% of the cases. Although this study could not statistically confirm the exact role of serology in detecting BHD, the data suggest that serology alone cannot be relied upon for diagnosing cerebral HD. Additionally, imaging modalities, including both CT and MRI, were indicated for the diagnosis of the disease in 95.5% of cases. The management of BHD typically involves a combination of surgical and adjunctive medical therapies. The treatment plan may vary depending on the size, number, location, and depth of invasion of the lesions into the brain parenchyma. Consequently, the prognosis of the disease can vary based on these factors. The most effective method is surgery. Although different surgical techniques have been investigated, there is consensus that intact cyst removal and total resection of the mass lesion without rupturing it or spilling its contents should be the core of the surgery. This approach is crucial in preventing perioperative complications, recurrence, and progression of the disease. The Dowling-Orlando technique, later modified by Arana-Iniguez and San Julian, is the most widely used surgical method for removing CNS hydatid cysts. This technique involves the formation of a hydrostatic assistant and continuous irrigation with hypertonic saline to dissect the cyst wall from the brain parenchyma, thereby achieving the intact removal of the cyst [26,42,53]. The location of the cyst, its size, adhesion to surrounding structures, multiplicity, and the presence of deep-seated lesions, especially in cases of alveolar E. multilocularis, can make the removal of the cyst intact challenging. The Dowling-Orlando technique may not be feasible in all cases of brain HD. In such situations, alternative methods aimed at minimizing the spillage of the cyst contents can be considered. The PAIR technique, which involves puncture and needle aspiration of the cyst, followed by the injection of a scolicidal solution for 20-30 minutes and cyst re-aspiration, has been reported as a reasonable approach [74,75,111].
Furthermore, the technique of burr-hole opening over the site of the cyst and the introduction of a cannula through the brain to drain the cyst, followed by removal of the cyst wall, has also been reported. However, this method of aspiration is discouraged unless total removal by other techniques is impossible. In patients with brain AE, radical excision should be performed for all accessible lesions. These procedures can be combined with the use of microsurgical and neuronavigation modalities to reduce perioperative complications [56,104]. Intraoperative cyst rupture is a common and serious event. Spillage of the cyst content into the brain tissue may lead to a fatal anaphylactic reaction, which is a chief cause of mortality during surgery. Furthermore, it increases the risk of high recurrence rates of the disease, particularly if the cyst is primary, as it is a fertile lesion [33,35]. The main reported early post-operative complications often arise due to the space left after the excision of large lesions. These may include subdural hematomas, hyperpyrexia, cerebral edema, cortical collapse, or even cardiorespiratory failure. Late post-operative complications such as porencephalic cyst, hydrocephalus, pneumocephalus, hemorrhage, seizures, and focal neurological deficits can occur in the days following surgery. These complications may require conservative management or further intervention [11,20,33]. Although the principal treatment of HD is surgery, pre-and post-operative adjunctive anthelmintic therapy, mainly with albendazole, may be considered. Albendazole can sterilize the cysts, decrease the tension in the cyst wall (thus reducing the risk of spillage during surgery and subsequently the risk of anaphylaxis and recurrence), and is also used for inoperable lesions. The optimal duration of treatment is still unclear, but recommended regimens involve albendazole taken orally at 10–15 mg/kg/day for 3–6 months, followed by a 'rest period' of 15 days after each month. Supportive medications can also be used to manage the presenting symptoms associated with the disease [12,93]. Among the several reviewed studies, a history of traumatic cyst rupture or iatrogenic cyst puncture during surgical procedures played a role in causing the recurrence of the disease [14,76,97]. In the present study, the primary treatment was surgical intervention in most cases (97.2%). The surgical approaches were commonly Dowling-Orlando or modified Arana-Iniguez (95.5%), while three cases (1.7%) underwent burr-hole surgery. In addition, five cases (2.8%) had been managed with conservative treatment only. The recurrence was reported in 13 cases (7.3%). Among them, six cases had intraoperative rupture of the cyst, and two had iatrogenic puncture of the cyst. No alveolar cases showed a recurrence. For this reason, this study recommends surgical intervention over conservative treatment. Follow-up for up to two years is recommended, especially in cases of giant hydatid disease or perioperative complications. In this systematic review, the mean follow-up period was 12 months. It has been reported that the majority of BHD cases can recover and survive with proper management [11,20]. Accordingly, the mortality rate in this study was only 3.4%. The major limitation of this study is the predominantly descriptive nature of the included studies, which may not yield reliable outcomes and can introduce bias. Further research employing rigorous study designs, such as trials comparing different surgical techniques for managing BHD, is recommended, particularly for the alveolar form.
Conclusion
Imaging modalities, such as CT and MRI, are the primary diagnostic tools for intra-parenchymal BHD, while serological tests alone are not reliable. Surgical intervention remains the definitive treatment for BHD. However, clinical diagnosis and treatment of AE continue to pose significant challenges. Therefore, in endemic regions, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving prognosis. A history of cyst rupture during surgery may increase the risk of recurrence, necessitating extensive follow-up.
Declarations
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval: Not applicable.
Patient consent (participation and publication): Not applicable.
Funding: The present study received no financial support.
Acknowledgements: None to be declared.
Authors' contributions: FHF and ASH were significant contributors to the conception of the study and the literature search for related studies. HOA and ABL involved in the literature review, study design, and manuscript writing. ZOKA, KAA, RJR, AKG, SMA, and ADA were involved in the literature review, the study's design, the critical revision of the manuscript, and data collection. FHF and HOA confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Use of AI: ChatGPT-4.0 was used to assist in language editing and improving the clarity of the manuscript. All content was reviewed and verified by the authors. Authors are fully responsible for the entire content of their manuscript.
Data availability statement: Not applicable.
References
- Alley Svrckova P, Nabarro L, Chiodini PL, Jäger HR. Disseminated cerebral hydatid disease (multiple intracranial echinococcosis). Practical neurology. 2019 Apr 1;19(2):156-63. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2018-001954
- Altibi AM, Qarajeh RA, Belsuzarri TA, Maani W, Kanaan TM. Primary cerebral echinoccocosis in a child: Case report–Surgical technique, technical pitfalls, and video atlas. Surgical Neurology International. 2016;7(Suppl 37):S893. doi:10.4103%2F2152-7806.194512
- Casulli A, Pane S, Randi F, Scaramozzino P, Carvelli A, Marras CE, Carai A, Santoro A, Santolamazza F, Tamarozzi F, Putignani L. Primary cerebral cystic echinococcosis in a child from Roman countryside: Source attribution and scoping review of cases from the literature. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2023 Sep 5;17(9):e0011612. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0011612
- Lakhdar F, Benzagmout M, Chakour K, el faiz Chaoui M. Multiple and infected cerebral hydatid cysts mimicking brain tumor: unusual presentation of hydatid cyst. Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery. 2020 Dec 1;22:100802. doi:10.1016/j.inat.2020.100802
- Binesh F, Mehrabanian M, Navabii H. Primary brain hydatosis. Case Reports. 2011; (2011): bcr0620103099. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2010.3099
- Saleh SM. Successful surgical management of intracerebral hydatid cyst in children: timing, procedure, and adjuvant treatment. Journal of Medicine in Scientific Research. 2020 Oct 1;3(4):303. doi: N/A
- Alomari M, Almutairi M, Alali H, Elwir J, Alola S, Alfattoh N, Alharthy N, Azzubi M. Primary giant cerebral hydatid cyst in an 8-year-old girl. Asian journal of neurosurgery. 2018 Sep;13(03):800-2. doi:10.4103/ajns.AJNS_240_16
- Hafedh, A.N., Aktham, A.A., Al-Sharshahi, Z.F., Al-Jorani, A.I., Albairamani, S., Alsubaihawi, Z.A., Al-Khafaji, A.O. and Hoz, S.S., 2021. Primary multiple cerebral hydatid disease in a young patient with surgically-treated intracerebral haemorrhage: A case report. Romanian Neurosurgery, pp.71-74. doi:10.33962/roneuro-2021-011
- Umut YA, Yavuz AR, AYDOSELI A, AKCAKAYA MO, SENCER A, Murat IM, HEPGUL K. Primary Multiple Cerebral Hydatid Disease: Still Symptomatic Despite Pathologically Confirmed Death of the Cyst. Turkish Neurosurgery.;23(4). doi:10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.5826-12.1
- Çavuşoğlu H, Tuncer C, Özdilmaç A, Aydin Y. Multiple intracranial hydatid cysts in a boy. Turkish neurosurgery. 2009 Apr 1;19(2). doi: doi: N/A
- Garg D, Jain G, Sinha V. A case report of primary brain hydatid cyst in a child. Iranian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2020 Jan 10;6(1):41-8. doi:10.32598/irjns.6.1.7
- Raouzi N, et al. Cerebral Hydatid Cysts: A Case Series. Int J Surg Surgical Tech 2019, 3(1): 000137. doi: N/A
- Assefa G, Biluts H, Abebe M, Birahanu MH. Cerebral hydatidosis, a rare clinical entity in Ethiopian teaching hospitals: case series and literature review. East and Central African Journal of surgery. 2011;16[2]:123-9. doi: N/A
- Tanki H, Singh H, Raswan US, Bhat AR, Kirmani AR, Ramzan AU. Pediatric intracranial hydatid cyst: a case series with literature review. Pediatric Neurosurgery. 2018 Sep 14;53(5):299-304. doi:10.1159/000488714
- Noori FA, Saheb AH. A giant cerebral hydatid cyst required urgent operation: case report. University of Thi-Qar Journal Of Medicine. 2019 Aug 4;17(1):183-93. https://doi.org/10.32792/jmed.v17i1.74
- NATH HD, BARUA KK, BARI MS, MURSALIN A, ALI MM. A Giant Hydatid Cyst at Right Frontoparietal Region: A Rare Case Report. Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience. 2015;31(2):116-20. doi:10.3329/bjn.v31i2.57384
- Panda NB, Batra Y, Mishra A, Dhandapani S. A giant intracranial hydatid cyst in a child: Intraoperative anaesthetic concerns. Indian J Anaesth. 2014 Jul;58(4):477-9. doi:10.4103/0019-5049.139018
- Sharifi G, Babamahmoodi A, Sabeti S, Hallajnejad M, Darazam IA. A middle-aged man with a mass in the brain and heart. Journal of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2023 Jul 5;13(2):90-. doi:10.5455/JMID.2023.v13.i2.7
- Aydin MD, Karaavci NC, Akyuz ME, Sahin MH, Zeynal M, Kanat A, Altinors MN. A new technique in surgical management of the giant cerebral hydatid cysts. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2018 May 1;29(3):778-82. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000004236
- Çakir M, Çalikoglu Ç, Yilmaz A. A Very Rare Complication of Cerebral Hydatid Cyst Surgery: Cortical Collapse. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2017 Oct-Dec;12(4):346-348. doi:10.4103/jpn.JPN_82_17.
- Ponnambath DK, Kaviyil JE, Raja K, Kesavapisharady K, Thomas B, Narasimhaiah D, Sehgal R, Kaur U. An unusual guest in an unusual location of the brain of a rural tribal man. Journal of The Academy of Clinical Microbiologists. 2022 Jan 1;24(1):44-7. doi:10.4103/jacm.jacm_9_22
- M. İzgi Et Al. , "Anesthetic management of a pediatric patient during surgical excision of primary cerebral hydatid cyst," Medicine Science International Medical Journal , vol.7, pp.443-445, 2018. doi:10.5455/medscience.2017.07.8799
- El Ouarradi A, Oualim S, Bensahi I, Elkouhen M, Abouloiafa I, Sabry M. Brain and Cardiac Concomitant Localization of the Hydatid Cyst. Case Reports in Pediatrics. 2020 Aug 18;2020. doi:10.1155/2020/4829496
- Baboli S, Baboli S, Meigooni SS. Brain hydatid cyst with atypical symptoms in an adult: a case report. Iranian Journal of Parasitology. 2016;11(3):422. doi: N/A
- Arega G, Merga G, Tafa G, Salah FO, Abebe G, Maru S, Ergete W. Temporoparietal brain hydatid cyst in an eight-year-old child: a rare case report. Pediatric health, medicine and therapeutics. 2022 Jan 1:361-5. doi:10.2147/PHMT.S390336
- Altaş M, Serarslan Y, Davran R, Evirgen Ö, Aras M, Yilmaz N. The Dowling-Orlando technique in a giant primary cerebral hydatid cyst: a case report. Neurologia i neurochirurgia polska. 2010;44(3):304-7. doi:10.1016/S0028-3843[14]60046-3
- Madeo J, Zheng X, Ahmed S, De Oleo RR. Primary cerebral echinococcosis presenting as long-standing generalized weakness. Germs. 2013;3(2):63. doi:10.11599%2Fgerms.2013.1038
- Menschaert D, Daron A, Frere J. Case report of cerebral cystic echinococcosis in a 5-year-old child. Frontiers in Tropical Diseases. 2023;4:1090644. doi:10.3389/fitd.2023.1090644
- Göktürk Ş, Göktürk Y. Cerebral echinococcus that can be confused with brain tumour: a case report. Folia Neuropathologica. 2023;61(1). doi:10.5114/fn.2023.131210
- Benhayoune O, Makhchoune M, Jehri A, Haouas MY, Naja A, Lakhdar A. Cerebral hydatid cyst during pregnancy: A case report. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2021;63:102161. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.02.007
- Vikas S, Preety S, Sanjeev P. Cerebral hydatid cyst: A case report. Acta Medica International. 2016;3(1):207-9. doi:10.5530/ami.2016.1.41
- Reddy OJ, Gafoor JA, Suresh B, Prasad PO. Cerebral hydatid disease: Is it primary or secondary?. Indian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2014;3(01):041-3. doi:10.4103/2277-9167.132004
- Al-Rawi WW, Al-Rawi FW. Cerebral Hydatid Disease Patients Admitted to Duhok City Hospitals: Management and Outcome. AMJ (Advanced Medical Journal). 2023;8(2):23-30. doi:10.56056/amj.2023.214
- Naderzadeh A, Ghanim SM, Keikhosravi E, Shojaeian R. Childhood refractory headache: Alarming sign of hydatid disease in endemic area. Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports. 2020;61:101610. doi:10.1016/j.epsc.2020.101610
- Shafiei R, Raeghi S, Jafarzadeh F, Najjari M, Ghatee MA, Shokri A. Three cases of brain hydatidosis in North Khorasan, Iran. Clinical case reports. 2022;10(7):e6095. doi:10.1002/ccr3.6095
- Nechi S, Gharbi G, Douggaz A, Belfekih H, Chaabane A, Mfarrej MK, Chelbi E. Multiple hydatid cyst disease revealed by an expansive intracranial process: A case report. Clinical Case Reports. 2023;11(3):e7102. doi:10.1002/ccr3.7102
- EKİCİ M, Ekici A, Per H, Tucer B, Kumandas S, Kurtsoy A. Concomitant heart and brain hydatid cyst without other organ involvement: a case report. DUSUNEN ADAM-JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY AND NEUROLOGICAL SCIENCES. 2011;24(2). doi:10.5350/dajpn2011240211
- Bagheri AB, Zibaei M, Arasteh MT. Cystic echinococcosis: a rare case of brain localization. Iranian Journal of Parasitology. 2017;12(1):152. doi: N/A
- Bušić Ž, Bradarić N, Ledenko V, Pavlek G. Cystic Echinococcosis of Lung and Heart Coupled with Repeated Echinococcosis of Brain–A Case Report. Collegium antropologicum. 2011;35(4):1311-5. doi: N/A
- Nashibi M, Tafrishinejad A, Khan ZH. Deep Seated Cerebral Hydatid Cyst and Its Anesthetic Considerations: A Case Report. Archives of Neuroscience. 2020;7(1). doi:10.5812/ans.100044
- Ammor H, Boujarnija H, Lamrani Y, Boubbou M, Kamaoui I, Maaroufi M, Tizniti S. Subdural hygroma as a complication of cerebral hydatid cyst surgery. 2014, doi: DOI: doi:10.1594/EURORAD/CASE.11928
- Alok R, Mahmoud J. Successful surgical treatment of a brain stem hydatid cyst in a child. Case Reports in Surgery. 2020 ;2020. doi:10.1155/2020/5645812
- Chatzidakis E, Zogopoulos P, Paleologos TS, Papageorgiou N. Surgical planning for the treatment of a patient with multiple, secondary, intracranial echinococcal cysts. The Surgery Journal. 2016 ;2(01):e7-10. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1570317
- Panagopoulos D, Gavra M, Stranjalis G, Boviatsis E, Korfias S, Karydakis P, Tmemistocleous M. Echinococcus Infestation of the Central Nervous System as the Primary and Solitary Manifestation of the Disease: Case Report and Literature Review. Medical Research Archives. 2023 ;11(1). doi:10.18103/mra.v11i1.3510
- Karaaslan A, Borekci A. Emergency surgical treatment in primary cerebral hydatid cyst: A case report and review of the literature. South Clin Ist Euras. 2017;28(2):143-6. doi:10.14744/scie.2017.09797
- Hajhouji F, Aniba K, Laghmari M, Lmejjati M, Ghannane H, Benali SA. Epilepsy: unusual presentation of cerebral hydatid disease in children. The Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;25. doi:10.11604%2Fpamj.2016.25.58.10706
- Tascu A, Ciurea AV, Vapor I, Iliescu A, Brehar F. Giant asymptomatic intracranial hydatid cyst in a 3 years old child: case report. Romanian Neurosurgery. 2010 :359-63. doi: N/A
- Kisti BY. Giant brain hydatid cyst in an adult: a new case report. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2021;45(1):76-9. doi:10.4274/tpd.galenos.2020.6921
- Ganjeifar B, Ghafouri M, Shokri A, Yazdi FR, Hashemi SA. Giant cerebral hydatid cyst: a rare case report. Clinical Case Reports. 2021;9(3):1774. doi:10.1002%2Fccr3.3908
- Nemati A, Kamgarpour A, Rashid M, Sohrabi Nazari S. Giant cerebral hydatid cyst in a child: A case report and review of literature. BJMP. 2010;3(3):a338. doi: N/A
- Abouei Mehrizi MA, Tavakolian A, Rezaee H, Keykhosravi E, Salahshoor Y. Giant Cerebral Hydatid Cyst in a Five-Year Old Child: A Case-Report. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2020;8(6):11485-91. doi:10.22038/ijp.2020.46683.3788
- Fakhouri F, Ghajar A, Mahli N, Shoumal N. Giant hydatid cyst in the posterior fossa of a child. Asian journal of neurosurgery. 2015;10(04):322-4. doi:10.4103/1793-5482.162719
- Ghasemi AA, Mohammadzade H, Mohammadi R. Giant hydatid cyst of the brain: Intact cyst removal in 8-year-old child. International Journal of Surgery Case Reports. 2023;106:108172. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108172
- Mallik J, Kumar A, Sahay CB, Minj TJ. Giant intracranial hydatid cyst: A report of two cases and literature review. Indian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2012;1(01):080-2. doi:10.4103/2277-9167.94378
- Arora SK, Aggarwal A, Datta V. Giant primary cerebral hydatid cyst: A rare cause of childhood seizure. Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences. 2014;9(1):73-5. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.131495
- Al-musawi AA, FICNS NF. Removal of brain hydatid cyst through burr-hole operation [case report]. Medical Journal of Babylon. 2015;12(2). doi:10.2139/ssrn.3568443
- Ghasemi AA. Hydatid Cyst of the Brain: A Case Report. Neurosurgery Quarterly. 2014;24(2):136-8. doi:10.1097/WNQ.0b013e31828db480
- Polat G, Ogul H, Sengul G. Hydatidosis following giant cerebral hydatid cyst operation. World neurosurgery. 2018 ;118:14-5. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2018.06.215
- Hmada S, Mesbahi T, Jehri A, Jouida A, Naja A, Amenzoui N, Lakhdar A. Pediatric brain hydatid cyst about two cases: Case report. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2022;78. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103806
- Senapati S, Parida D, Pattajoshi A, Gouda A, Patnaik A. Primary hydatid cyst of brain: Two cases report. Asian journal of neurosurgery. 2015;10(02):175-6. doi:10.4103%2F1793-5482.152109
- Imperato A, Consales A, Ravegnani M, Castagnola E, Bandettini R, Rossi A. Primary hydatid cyst of the brain in a child: A case report. Polish Journal of Radiology. 2016;81:578. doi:10.12659%2FPJR.898619
- Ramosaço E, Kolovani E, Ranxha E, Vyshka G. Primary multiple cerebral hydatid cysts in an immunocompetent, low-risk patient. IDCases. 2020;21:e00882. doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00882
- Ravanbakhsh N, Rabiee N, Ahmadi J. Primary solitary hydatid cyst of brain in a 12-year-old boy: A Case Report. Iranian Journal of Parasitology. 2019;14(4):668. doi: N/A
- Pulavarty P, Korde P, Rathod S, Patnaik J, Domakunti R, Singh SP. Primary solitary hydatid disease of brain in a 16-year-old girl: a case report. Pan African Medical Journal. 2022;42(1). doi:10.11604/pamj.2022.42.195.34744
- Shastry S, Anandam G, Kumari BS, Sreelatha K. Primary cerebral hydatid cyst in a child. Medical Journal of Dr. DY Patil University. 2015;8(2):214-6. doi:10.4103/0975-2870.153168
- Chen S, Li N, Yang F, Wu J, Hu Y, Yu S, Chen Q, Wang X, Wang X, Liu Y, Zheng J. Medical treatment of an unusual cerebral hydatid disease. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2018;18:1-4. doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2935-2
- Kaushik S, Sunanadan B, Harsh J, Laxminarayan T. Multicystic Cerebral Hydatid Cyst: Uncommon Presentation of A Rare Disease. Nepal Journal of Neuroscience. 2015;12(1):49-51. doi:10.3126/njn.v12i1.15928
- Wani NA, Kosar TL, Khan AQ, Ahmad SS. Multidetector-row computed tomography in cerebral hydatid cyst. Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice. 2010;1(02):112-4. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.71728
- Armanfar M, Motavallihaghi S, Heidari S, Ghasemikhah R. Multiple cerebral hydatid cysts: A rare case report. Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery. 2024;36:101878. doi:10.1016/j.inat.2023.101878
- Khan MB, Riaz M, Bari ME. Multiple cerebral hydatid cysts in 8-year-old boy: A case report and literature review of a rare presentation. Surgical Neurology International. 2015;6. doi:10.4103%2F2152-7806.161785
- Charles KK, Didier N. MULTIPLE CEREBRAL HYDATID CYSTS WITH CALCIFICATION: ABOUT A CASE OF A YOUNG ADULT. Revue Médicale des Grands Lacs. 2020;11(1). doi:10.7759/cureus.25529
- Garg M, Sarma P, Chaturvedi S, Pant I. Multiple Primary Bilateral Cerebral Echinococcosis in an Adult: A Neurological Rarity. Asian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2022;17(04):647-50. doi:10.1055/s-0042-1757725
- Abuhajar RM. Multiple Primary Cerebral Hydatid Disease in Adult; CT and MRI Diagnosis; Case Report and Review of Literature.2015 MMSJ Vol.2 Issue.2. doi: N/A
- Umerani MS, Abbas A, Sharif S. Intra cranial hydatid cyst: A case report of total cyst extirpation and review of surgical technique. Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice. 2013;4(S 01):S125-8. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.116445
- Touzani S, Bechri B, Joulali T, Berdai MA, Labib S, Harandou M. Intracerebral hydatid cyst: A rare cause of neurosurgical emergency. Int J Case Rep Images 2016;7(11):758–761. doi:10.5348/ijcri-2016133-CR-10721
- Kibzai Ms, Anwar K, Islam M, Shahid S. Intracranial Hydatid Cyst: A Case Report of Three Cases. Pakistan Journal Of Neurological Surgery. 2018;22(3):115-22. doi: N/A
- Duransoy YK, Mete M, Barutçuoğlu M, Ünsal ÜÜ, Selçuki M. Intracranial hydatid cyst is a rare cause of midbrain herniation: A case report and literature review. Journal of pediatric neurosciences. 2013;8(3):224-7. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.123683
- Qureshi PA, Panhwar IA, Kaimkhani MT, Qureshi PA. Intraventricular And Intrraparenchymal Hydatid Cysts: An Unusual Site Of Echinococcosis And A Rare Cause Of Childhood Seizures. PJR. 2019;29(1). doi: N/A
- Senol YC, Ozkan ND, Guresci S, Daglioglu E, Belen AD. Isolated Cerebral Cyst Hydatid Removal with Dowling's Technique in a 6-Year-Old Pediatric Patient: Case Report. Asian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2023;18(02):372-6. doi:10.1055/s-0043-1768600
- Kandemirli SG, Cingoz M, Olmaz B, Akdogan E, Cengiz M. Cerebral hydatid cyst with intraventricular extension: a case report. Journal of tropical pediatrics. 2019;65(5):514-9. doi:10.1093/tropej/fmy080
- Bahannan AA, Badheeb AM, Haroun BO, Barabba RO. Cerebral Hydatid Cyst with Vestibular and Neurologic Manifestations. HJMS-Hadramout Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012;1(1):35-7. doi:10.12816/0005931
- Kumar A, Suman S, Priyanka GN, Singh R. Cerebral hydatid disease: CT and MR imaging findings. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2014;3(58):13062-71. doi:10.57187/smw.2004.10711
- Agrawal V, Giri P. Largest intracranial calcified hydatid cyst: A case report with review of literature. Asian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2020;15(03):713-5. doi:10.4103/ajns.AJNS_143_20
- Mustafa MK, Matti WE, Kadhum HJ, Kareem ZM, Alsubaihawi ZA, Al-Sharshahi ZF, Hoz SS. Giant cerebral hydatid cyst manifesting as seizures in a child: A case report and literature review. Indonesian Journal of Neurosurgery. 2022;5(2):51-5. doi:10.15562/ijn.v5i2.174
- Ijaz L, Mirza B, Nadeem MM, Saleem M. Simultaneous giant hydatid cysts of brain and liver. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25(Suppl 1):S53-5. doi: N/A
- Borni M, Souissi G, Taallah M, Abdelmouleh S, Ayadi A, Boudawara MZ. Early postoperative intra-axial dissemination of a pediatric extradural and complicated hydatid cyst. Child's Nervous System. 2024;40(2):321-5. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3143624/v1
- Kojundzic SL, Dolic K, Buca A, Jankovic S, Besenski N. Hydatid disease with multiple organ involvement: a case report. Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2010;3(2):154-8. doi:10.3889/MJMS.1857-5773.2010.0094
- Siyadatpanah A, Brunetti E, Emami Zeydi A, Moghadam YD, Agudelo Higuita NI. Cerebral cystic echinococcosis. Case Reports in Infectious Diseases. 2020;2020. doi:10.1155/2020/1754231
- Akrim Y, Barkate K, Arrad Y, Ghannane H, El Hakkouni A. Multiple cerebral hydatid cysts: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14(5). doi:10.7759/cureus.25529
- Zeynal M, Akyüz ME, Şahin MH, Alay H, Karadağ MK, Kadıoğlu HH, Kara CF, Elveren M. A rare disease: a single-center experience of cerebral alveolar echinococcosis in 12 operated patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(1):426-30. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202301_30898
- Ozdol C, Yildirim AE, Daglioglu E, Divanlioglu D, Erdem E, Belen D. Alveolar hydatid cyst mimicking cerebellar metastatic tumor. Surgical Neurology International. 2011;2. doi:10.4103%2F2152-7806.76281
- Ma Z, Ma L, Ni Y. Cerebral alveolar echinococcosis: a report of two cases. Clinical neurology and neurosurgery. 2012;114(6):717-20. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.12.004
- Mokhtari H, Sadeghdoust M, Aligolighasemabadi F, Hashemiattar A, Ariabod V, Rahighi S. Neurological disorders caused by two cerebral alveolar hydatid cysts in an old woman: a rare case report. Oxford Medical Case Reports. 2017;2017(8):omx046. doi:10.1093/omcr/omx046
- Benzagmout M, Maaroufi M, Chakour K, Chaoui ME. Atypical radiological findings in cerebral hydatid disease. Neurosciences Journal. 2011;16(3):263-6. doi: N/A
- Ray M, Singhi PD, Pathak A, Khandelwal NK. Primary multiple intracerebral echinococcosis in a young child. Journal of tropical pediatrics. 2005;51(1):59-61. doi:10.1093/tropej/fmh059
- YİŞ U, UÇAR MD, BAŞAR N, BAŞTEMİR M. Gigantic hydatid cyst of the brain. Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi. 2008;22(3):161-2. doi: N/A
- Per H, Kumandaş S, Gümüş H, Kurtsoy A. Primary soliter and multiple intracranial cyst hydatid disease: Report of five cases. Brain and Development. 2009;31(3):228-33. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2008.03.009
- Farid R, Farideh N. Primary cerebral hydatid cyst: two cases report. Iranian Journal of Pediatrics. 2008; 18 (1): 83-86. doi: N/A
- Balak N, Cavumirza C, Yldrm H, Özdemir S, Knay D. Microsurgery in the removal of a large cerebral hydatid cyst: technical case report. Operative Neurosurgery. 2006;59(4):ONS-E486. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000232766.77094.79
- Najjar MW, Rajab Y, El-Beheiri Y. Intracranial hydatid cyst. Dilemma in diagnosis and management. Neurosciences Journal. 2007;12(3):249-52. doi: N/A
- Tatli M, Guzel A, Altinors N. Large primary cerebral hydatid cysts in children. Neurosciences Journal. 2006;11(4):318-21. doi: N/A
- Yurt A, Avcı M, Selçuki M, Özer F, Çamlar M, Uçar K, Taşlı F, Altınörs N. Multiple cerebral hydatid cysts: report of a case with 24 pieces. Clinical neurology and neurosurgery. 2007;109(9):821-6. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2007.07.011
- AYDIN MD, AYDIN N. A cerebral hydatid cyst case first presenting with Gerstmann's Syndrome: A case report and literature review. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences. 2003;33(1):57-60. https://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/medical/vol33/iss1/11
- Tuzun Y, Kadioglu HH, Izci Y, Suma S, Keles M, Aydin IH. The clinical, radiological and surgical aspects of cerebral hydatid cysts in children. Pediatric neurosurgery. 2004;40(4):155-60. doi:10.1159/000081932
- Bakaris S, Sahin S, Yuksel M, Karabiber H. A large cerebral hydatid cyst associated with liver cyst. Annals of tropical paediatrics. 2003;23(4):313-7. doi:10.1179/027249303225007761
- Guney O, Ozturk K, Kocaogullar Y, Eser O, Acar O. Submandibular and intracranial hydatid cyst in an adolescent. The Laryngoscope. 2002;112(10):1857-60. doi:10.1097/00005537-200210000-00029
- Önal Ç, Yakinci C, Erten F, Erguvan R, Çayli S, Gül A, Aydin E. Supratentorial hydatid cyst with cerebellar signs: a rare case of diaschisis. Child's nervous system. 2001;17:746-9. doi:10.1007/s003810100485
- Muthusubramanian V, Pande A, Vasudevan MC, Ravi R. Surgical management of brainstem hydatid cyst—an unusual site. Surgical neurology. 2009;71(1):103-6. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2007.06.077
- Kabatas S, Yilmaz C, Cansever T, Gulsen S, Sonmez E, Altinors MN. The management of a complicated brain hydatid cyst: case report. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2009;43(6):575-8. doi: N/A
- Menkü A, Kurtsoy A, Tücer B, Durak Ac, Akdemir H. Calcified cerebral hydatid cyst following head trauma: case report. Turkish Neurosurgery. 2004;14(1-2) . doi: N/A
- Anvari M, Amirjamshidi A, Abbassioun K. Gradual and complete delivery of a hydatid cyst of the brain through a single burr hole, a wrong happening!. Child's Nervous System. 2009;25:1639-42. doi:10.1007/s00381-009-0937-0
- Karadağ Ö, Gürelik M, Özüm Ü, Göksel HM. Primary multiple cerebral hydatid cysts with unusual features. Acta neurochirurgica. 2004;146:73-7. doi:10.1007/s00701-003-0169-0.
- Kakamad FH, Abdalla BA, Abdullah HO, Omar SS, Mohammed SH, Ahmed SM, et al. Lists of predatory journals and publishers: a review for future refinement. European Science Editing. 2024;50: e118119. doi:10.3897/ese.2024.e118119
- Kakamad FH, Anwar KA, Ahmed HK, Habibullah IJ, Kaka Ali HH, Nasralla HA, et al. Risk factors associated with human echinococcosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in VeterinaryScience.2024;11:1480579.doi:10.3389/fvets.2024.1480579
- Nasralla HA, Abdalla BA, Abdullah HO, Ahmed SM, Kakamad FH, Mohammed SH, et al. Current Perspectives on Cystic Echinococcosis: A Systematic Review. Judi Clin. J. 2025;1(1):12-26. doi:10.70955/JCJ.2025.1

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

